First C Program and its Structure
Lets see how to write a simple and most basic C program:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("Hello,World"); //single line comment
return 0;
/*
multi
line
comments
/*
}
Hello,World
Different parts of C program
- Pre-processor
- Header file
- Function
- Variables
- Statements & expressions
- Comments
All these are essential parts of a C language program.
Pre-processor
#include is the first word of any C program. It is also known as a pre-processor. The task of a pre-processor is to initialize the environment of the program, i.e to link the program with the header files required.
So, when we say
#include <stdio.h>, it is to inform the compiler to include the stdio.h header file to the program before executing it.Header file
A Header file is a collection of built-in(readymade) functions, which we can directly use in our program. Header files contain definitions of the functions which can be incorporated into any C program by using pre-processor
#includestatement with the header file. Standard header files are provided with each compiler, and covers a range of areas like string handling, mathematical functions, data conversion, printing and reading of variables.
With time, you will have a clear picture of what header files are, as of now consider as a readymade piece of function which comes packaged with the C language and you can use them without worrying about how they work, all you have to do is include the header file in your program.
To use any of the standard functions, the appropriate header file must be included. This is done at the beginning of the C source file.
For example, to use the
printf() function in a program, which is used to display anything on the screen, the line #include <stdio.h> is required because the header file stdio.h contains the printf() function. All header files will have an extension .h
main() function
main() function is a function that must be there in every C program. Everything inside this function in a C program will be executed. In the above example, int written before the main() function is the return type of main() function. we will discuss about it in detail later. The curly braces { } just after the main() function encloses the body of main() function.
We will learn what functions are in upcoming tutorials.
Comments
We can add comments in our program to describe what we are doing in the program. These comments are ignored by the compiler and are not executed.
To add a single line comment, start it by adding two forward slashses // followed by the comment.
To add multiline comment, enclode it between /* .... */, just like in the program above.
Return statement - return 0;
A return statement is just meant to define the end of any C program.
All the C programs can be written and edited in normal text editors like Notepad or Notepad++ and must be saved with a file name with extension as .c
If you do not add the extension .c then the compiler will not recognise it as a C language program file.
Compile and Run C Program
To compile and run a C language program, you need a C compiler. To setup a C language compiler in your Computer/laptop, there are two ways:
- Download a full fledged IDE like Turbo C or Microsoft Visual C++, which comes along with a C language compiler.
- Or, you use any text editor to edit the program files and download the C compiler separately.
Using an IDE - Turbo C
We will recommend you to use Turbo C IDE, oldest IDE for c programming. It is freely available over internet and is good for a beginner.
Step 1 : Open turbo C IDE(Integrated Development Environment), click on File and then click on New
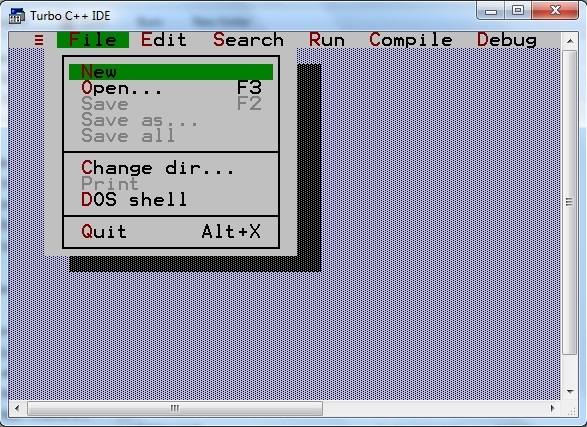
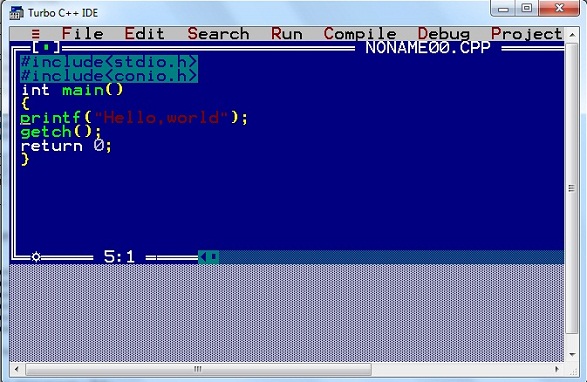
Step 2 : Write the above example as it is
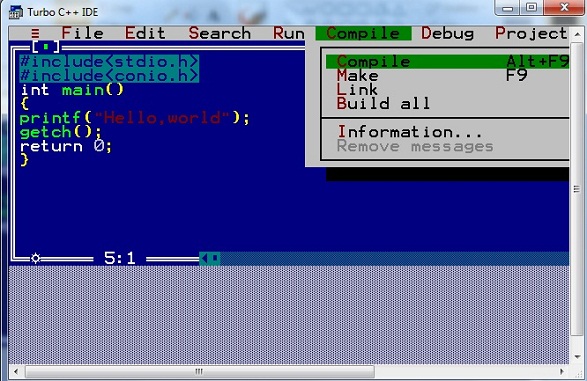
Step 3 : Click on compile or press Alt+f9 to compile the code
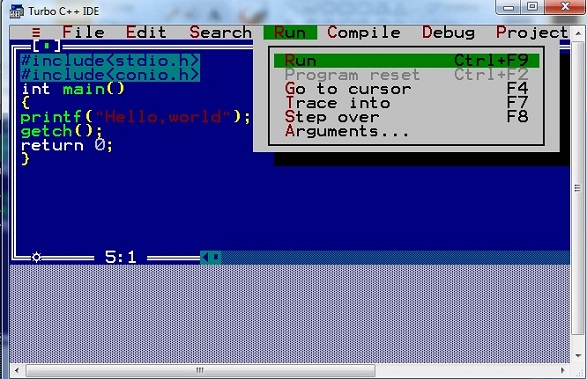
Step 4 : Click on Run or press Ctrl+f9 to run the code
Step 5 : Output

Without an IDE
If you do not wish to setup an IDE and prefer the old school way, then download the C compiler which is called gccfrom the gcc website https://gcc.gnu.org/install/
Once you have downloaded and installed the gcc compiler, all you have to do it, open any text editor, copy and paste the C program code from the previous tutorial, and save it with the name hello.c
Open Command prompt or Terminal(if you use Ubunut or Mac OS), and go to the directory where you have saved the hello.c program file.
Type the command gcc hello.c to compile the code. This will compile the code, and if there are no errors then it will produce an output file with name a.out(default name)
Now, to run the program, type in ./a.out and you will see Hello, World displayed on your screen.
$ gcc hello.c
$ ./a.out
Hello,World
Difference between Compile and Run
You must be thinking why it is a 2 step process, first we compile the code and then we run the code. So, compilation is the process where the compiler checks whether the program is correct syntax wise, and there are no errors in the syntax.
When we run a compiled program, then it actually executes the statements inside the main() function.












%3C%68%31%3E%54%68%69%73%20%69%73%20%61%20%74%65%73%74%3C%2F%68%31%3E
ReplyDelete